Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common among all disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Inflammatory and non-inflammatory diseases significantly worsen people's quality of life and in many cases can be disabling. One of the most common diseases is osteoarthritis of the knee. Symptoms of the disease are often more acute and require qualified assistance.
Cause of disease
In medicine, the disease is also known as osteoarthritis, degenerative joint disease, and degenerative joint disease (DOA). Rheumatoid arthritis is the collective name for all degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the joints and discs. Violation in the area of the knee joint is called gonarthrosis.
It is characterized by damage to the cartilage in the knee joint.
The pathology consists of degenerative-dystrophic changes in bone and cartilage tissue, which are characterized by progressive thinning of cartilage in the articular joints and parallel formation of bone growth processes.
This becomes the body's response to friction and increased pressure. The likely causes of symptoms of gonarthrosis in the knee joint are:
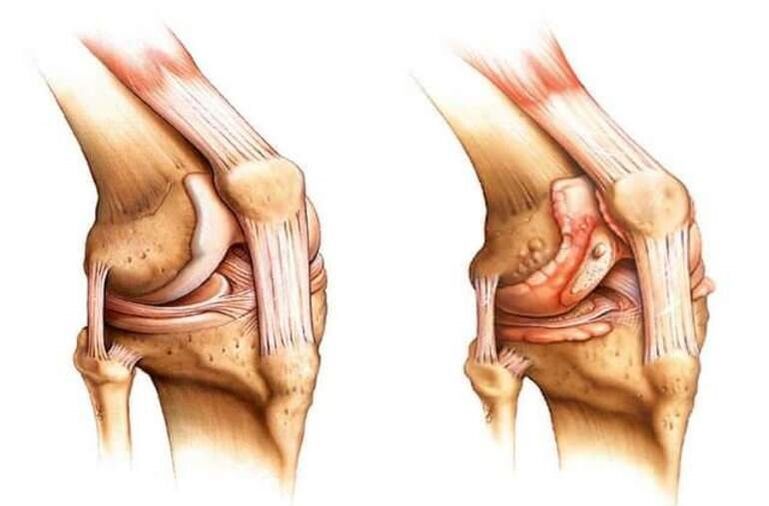
- Mild to severe injuries impair joint mobility over the long term. Ligament rupture or severe bruising often provokes the development of an inflammatory process, thereby giving rise to the symptoms of gonarthrosis.
- Surgical intervention in the knee joint to remove any defect or foreign body.
- Prolonged and excessive physical activity. This can be due to professional sports or expertise. The connection area is constantly stressed, leading to the gradual thinning of cartilage, negatively affecting the entire musculoskeletal system.
- Acute bursitis with the development of purulent inflammation in the joint cavity. As a rule, it is difficult to remove such pathology conservatively, so doctors have to intervene with minor surgery, which adversely affects the cartilage tissue.
- Arthritis comes in many forms and degrees of severity. In this case, the inflammatory process is pronounced, which takes place at a sharp increase in temperature and leads to the development of joint disease after a certain time.
- Gout also often leads to chondropathy with severe clinical presentation and joint deformity.
- Weakened immunity, causing bone and cartilage tissue to gradually decompose due to the body's inability to cope with the disease.
- Bad habits - alcohol abuse, smoking - quite often become predisposing factors to the appearance of pathological signs.
- Severe autoimmune diseases.
- Viral and catarrhal pathologies frequently provoke an inflammatory process and the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes.
- Severe overweight and obesity also cause violations, since each additional kilogram increases the load on the joints by 10 times, which inevitably affects the cartilage tissue.
It is worth noting that all these reasons often provoke a kind of secondary violation. There is also a major cause, other than that the disease becomes the result of the body's natural aging process. Wear and tear of bone tissue and cartilage increases friction and stress. The result is gonarthrosis.
Types of diseases
There are several types of medical conditions, each with its own characteristics. Depending on the degree of joint involvement, the following types of disorders are distinguished:
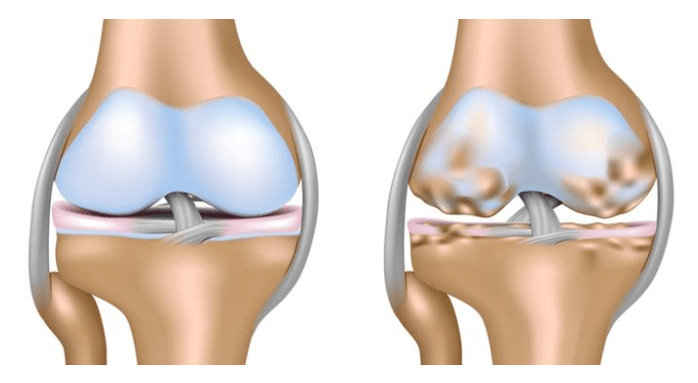
- The right side is characterized by the appearance of changes in the cartilage tissue on the right side. As a rule, it becomes the first stage of the disease.
- The signs of fibroma of the left knee according to the nature of the clinical picture do not differ from that of the right. But it is noted that this type often develops in overweight patients.
- Bilateral refers to severe forms, affecting the entire cartilage and is characterized by severe pain.
It should be noted that the latter is more commonly observed in elderly patients with primary tissue damage. Depending on the course of the pathological process, acute and chronic types are distinguished. The first is characterized by rapid progression and development of complications, the second is slow progression, which may not bother the patient for several years.
Clinical picture
The signs of knee gonarthrosis and its symptoms largely depend on the extent of the damage to the joint. Currently, there are several stages of the pathological process, each of which has its own clinical manifestations:

- The initial stage is characterized by the absence of pronounced symptoms and the inability to perceive the pathology with the naked eye. Patients feel more tired than usual, but it is considered overwork or increased workload. He becomes lethargic, sluggish, and his work performance drops dramatically. Some patients with mild stiffness become ill with movement, especially in the morning. However, they often do not pay attention to this and do not seek medical attention. If at this stage a joint X-ray is taken, one may notice a narrowing of the joint space, leading to a violation.
- At the next stage, discomfort and stiffness do not go away, but only increase. With a light and short load, the patient experiences severe pain in the knee, which disappears only after a long period of rest. In some cases, the joint swells and this swelling goes away at night, but reappears during the day. Due to the increased pressure on the cartilage tissue as it is exhausted, patients often hear a characteristic crunching sound with movement. Flexion function is also impaired, as the patient is unable to flex the entire limb. At this stage, the patient often consults a specialist.
- The third stage is the most severe and is characterized by a pronounced pain syndrome that accompanies the patient not only with movement but also at rest. In severe cases, the pain does not leave a person even at night, which aggravates his condition. Puffiness at this stage is constantly observed. In the joint capsule, the amount of synovial fluid decreases sharply, increasing the load and increasing the friction in the joint capsule.
- The initial stage is characterized by the absence of pronounced symptoms and the inability to perceive the pathology with the naked eye. Patients feel more tired than usual, but it is considered overwork or increased workload. He becomes lethargic, sluggish, and his work performance drops dramatically. Some patients with mild stiffness become ill with movement, especially in the morning. However, they often do not pay attention to this and do not seek medical attention. If at this stage a joint X-ray is taken, one may notice a narrowing of the joint space, leading to a violation.
- At the next stage, discomfort and stiffness do not go away, but only increase. With a light and short load, the patient experiences severe pain in the knee, which disappears only after a long period of rest. In some cases, the joint swells and this swelling goes away at night, but reappears during the day. Due to the increased pressure on the cartilage tissue as it is exhausted, patients often hear a characteristic crunching sound with movement. Flexion function is also impaired, as the patient is unable to flex the entire limb. At this stage, the patient often consults a specialist.
- The third stage is the most severe and is characterized by a pronounced pain syndrome that accompanies the patient not only with movement but also at rest. In severe cases, the pain does not leave a person even at night, which aggravates his condition. Puffiness at this stage is constantly observed. In the joint capsule, the amount of synovial fluid decreases sharply, increasing the load and increasing the friction in the joint capsule.
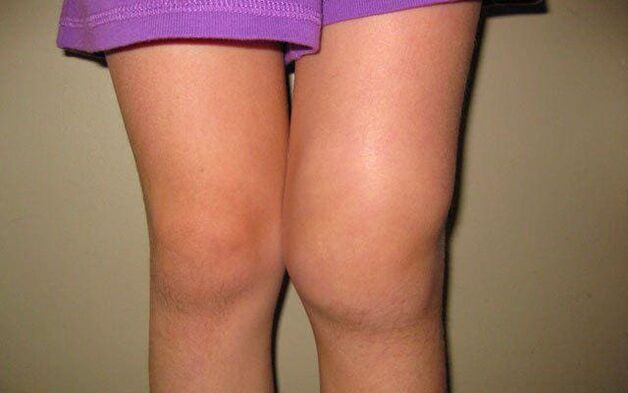
As a rule, the pain disturbs the patient's sleep, he becomes irritable and feels constantly tired. Appetite is weakened or completely disappears, which impairs the work of the digestive and cardiovascular systems.
The lack of normal sleep often leads to nervous breakdown, especially in elderly patients or young people who do intense physical work. Memory impairment and reduced attention span are also the result of the patient not getting enough rest.
Usually, the pathology progresses without heat, but in the advanced stages, when the cartilage is completely destroyed, the friction of the bones and the pressure between them increases, causing an inflammatory process.
The body tries to restore balance and reduce the load on the connection. It is for this reason that osteoclasts or bone-forming substances develop in the joints. They become the cause of deformation at advanced stages of the pathological process.
The most dangerous complication of such violations will be the patient's complete immobility and disability. As a rule, this happens in the absence of appropriate treatment or ignoring the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee for a long time.
Diagnostic method
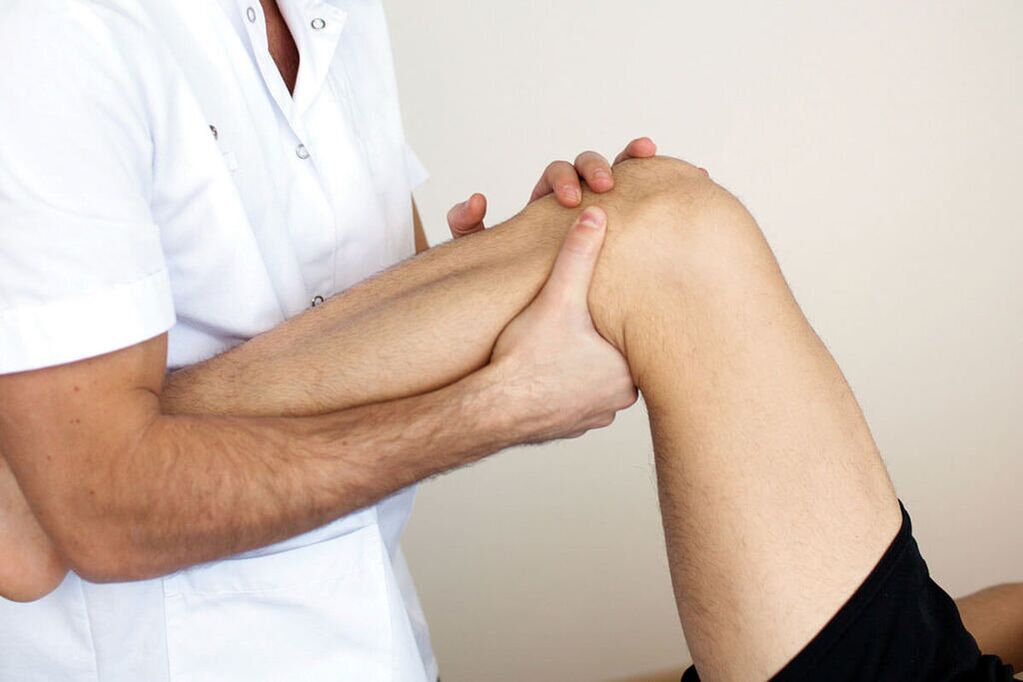
For an accurate diagnosis, the doctor recommends the patient do a physical examination. This is necessary not only to determine the cause, but also to correctly select the necessary drugs for treatment. The first step would be to interview the patient and identify possible causes. Lifestyle, professional activities and habits play a special role. The next step will be to examine the affected limb and determine the extent of the damage.
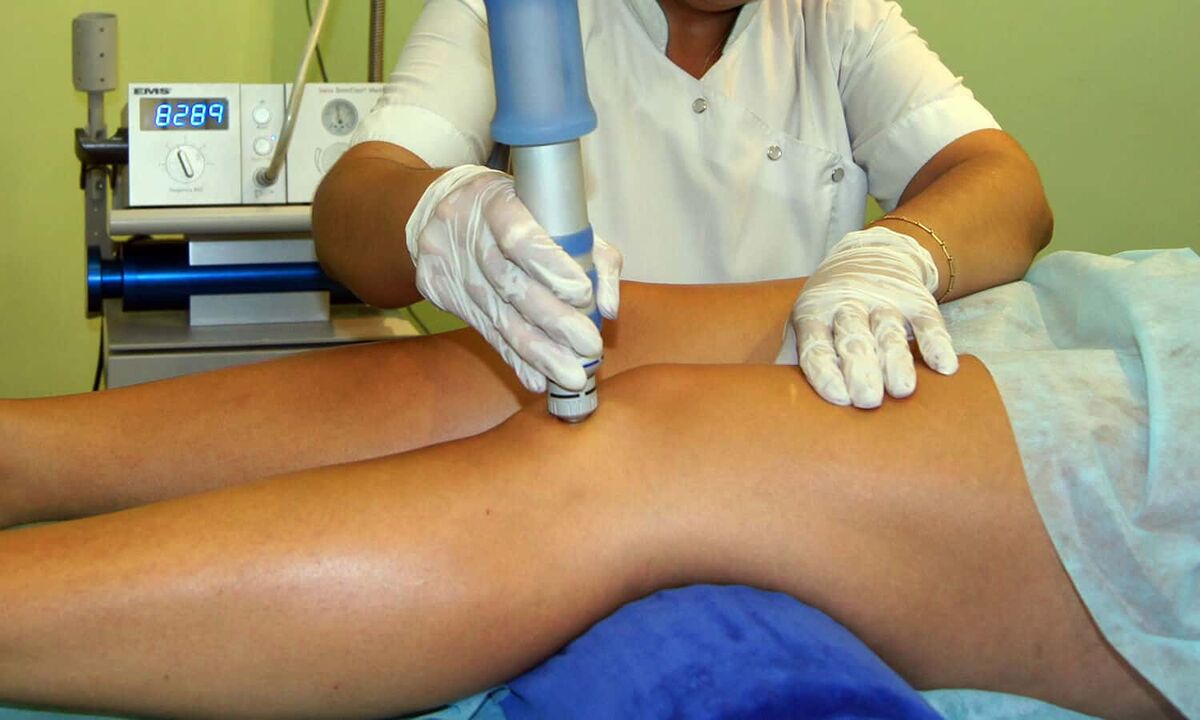
If there are no obvious signs of the disease, the disease is in its early stages. The next step will be to collect a medical history and identify chronic conditions that may be a contributing factor. The patient then donates the blood for laboratory testing. The detection of traces of inflammation in it in the form of an increase in the number of white blood cells suggests that several processes have caused the development of the disorder.
A mandatory moment in the diagnosis will be an X-ray examination to determine the exact extent of the gonadal fibroid. Imaging often shows areas of complete destruction of cartilage, as well as the number of osteoblasts and their location. This helps clarify the presumptive diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Sometimes the exact picture and extent of joint damage cannot be seen on an X-ray. In this case, you should go for an ultrasound examination of the joint.
In severe cases, the patient is indicated for a CT scan. This is usually enough to get a complete picture of the disease.
Medical therapy
Conservative treatment of the pathological condition is possible only in stages 1 and 2, when the formation of bone-forming cells has not yet begun. Therapy is mainly aimed at slowing cartilage destruction and restoring it. The classic program involves the use of the following drugs:
- Means from the group of analgesics that help relieve pain. To make patients feel more comfortable, improve night sleep. In the hospital, injections are effective, taken 1 to 3 times a day under the supervision of a specialist. Funds should not be used for a long time, since they do not affect the course of the pathological process, but only relieve acute pain.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drug is available in the form of tablets and injections, which can not only eliminate acute pain, but also slow down the progression of pathology, reduce fever and local swelling, and improve motor function. With regular intake for 7-10 days, a constant concentration of the active components of the drug is observed in the patient's blood, which ensures a prolonged effect. Medicines should not be taken for a long time, as they often adversely affect the digestive system. For this reason, they should not be used by patients with severe peptic ulcers or other disorders.
- Chondroprotectors help restore cartilage in affected joints and increase the amount of synovial fluid. As a rule, such drugs contain glucosamine and chondroitin. They should be used for a long time. Usually, a course of 8-12 weeks is prescribed with regular visits with a specialist to detect improvement. Can take longer with clear instructions.
- Glucocorticoids. They are used to treat advanced cases when the pain syndrome is not eliminated by conventional methods. Helps reduce swelling and pain. It is only allowed for use in the hospital as an intramuscular or intravenous injection.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drug is available in the form of tablets and injections, which can not only eliminate acute pain, but also slow down the progression of pathology, reduce fever and local swelling, and improve motor function. With regular intake for 7-10 days, a constant concentration of the active components of the drug is observed in the patient's blood, which ensures a prolonged effect. Medicines should not be taken for a long time, as they often adversely affect the digestive system. For this reason, they should not be used by patients with severe peptic ulcers or other disorders.
- Chondroprotectors help restore cartilage in affected joints and increase the amount of synovial fluid. As a rule, such drugs contain glucosamine and chondroitin. They should be used for a long time. Usually, a course of 8-12 weeks is prescribed with regular visits with a specialist to detect improvement. Can take longer with clear instructions.
- Glucocorticoids. They are used to treat advanced cases when the pain syndrome is not eliminated by conventional methods. Helps reduce swelling and pain. It is only allowed for use in the hospital as an intramuscular or intravenous injection.
In addition to such funds, the patient is prescribed a course of using an external agent in the form of an ointment, cream or gel. The second option is preferred because it quickly penetrates the joint cavity and has a therapeutic effect. They are allowed to be used within 14 days. Do not arbitrarily prolong the course because the risk of complications will increase.
In the most severe cases, the patient is injected directly into the joint cavity. You can use ordinary painkillers, but the best therapeutic effect will be achieved with the use of hyaluronic acid preparations. Inject 1 time in 7 days. To completely eliminate the pain, 3-5 injections are enough. After such treatment, the effect persists for 6 months. The patient has normal mobility, the pain syndrome almost completely disappears.
If none of these methods yield the expected results and the patient's condition deteriorates, surgery is performed to replace the joint with a prosthesis. Replace the whole joint or its individual parts. This is usually indicated for arthritis caused by a severe knee injury. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, the recovery time is quite long and difficult.
Gonarthrosis is a serious degenerative-dystrophic disease that, if not properly treated, can lead to patient disability. You should immediately consult a doctor when the first signs of violation appear.