The spine is a unique biodynamic system; it is able to withstand loads without damage, but, like any structure, it wears out over time. During youth, a steady state is maintained thanks to rapid regeneration, but after 50 years, their supply is gradually depleted, leading to the formation of osteonecrosis.
Cartilage degeneration is the most common degenerative-dystrophic disease of the spine, and as it progresses, it will spread to neighboring structures of the spinal segment.
Developmental theories
The cause of osteonecrosis is unknown. Existing theories about the development of this disease:
- Metabolically.Changes in the metabolism of the intervertebral disc due to dehydration (water content when young is 88%, with age the water content decreases to 60%).
- Blood vessel.Changes in spinal circulation (occurs in adulthood, but can develop earlier due to trauma, metabolic disorders, infections).
These theories are sometimes combined into one - degeneration, which is based on violations of nutrition, especially in nonvascular tissues. In childhood, there is a network of blood vessels in the intervertebral discs, but after the complete formation of the spinal structure, this network is closed by connective tissue.
- Hormone theorycause more controversy. Hormonal conditions play a role in the development of osteonecrosis, but it would be inappropriate to refer solely to hormone levels. This theory is most suitable for postmenopausal women.
- Mechanics theorytalks about the connection between the occurrence of osteonecrosis and overload of certain parts of the spine.
- Anomaly theory- a separate case from the theory of mechanics. Abnormalities of the vertebral bodies, fusion of the vertebral bodies, and non-fusion of the vertebral arch due to inappropriate biomechanics will stimulate overload of the vertebral discs and cause destruction. bone tissue.
These theories have a right to exist, but none of them is universal. It would be more correct to call osteoarthritis a multifactorial disease, characterized by genetic predisposition and provoking factors.
Factors that contribute to the development of the disease
- Gravity coefficient: For the spine, any non-physiological displacement is nothing more than a trigger for various muscle reactions.
- Dynamic factor:The greater and longer the load on the spine, the more susceptible it is to injury (people are more likely to be forced into long-term positions, lifting heavy objects continuously).
- Metabolic disorders:Inadequate spinal nutrition due to autoimmune disorders, toxic effects.
It is known that eating food with an aluminum plate will lead to its accumulation in the bones, which will then contribute to the formation of osteoarthritis. Eating food from dishes made of aluminum and iron alloys has a negative effect on the human body. When preparing food, microparticles enter the digestive tract and, since they also contain lead, this metal accumulates in the body, intoxication is manifested by neurofibromatosis (deformed changes in the body). defect in tissue at the junction of tendon and muscle).
- Genetic factors.Each person has a unique level of flexibility, which is directly correlated with the ratio of fibers in the connective tissue (collagen and Elastin) and is genetically inherited. Despite all of the above, there are still fiber ratio standards, deviations of which lead to faster wear of the spine.
- Biomechanical factors- non-physiological movements at the articular surfaces of the spine. The cause is muscle atrophy (clinical symptoms are pain when bending or turning).
- Sterile inflammatory factors– usually a rapid inflammatory process in the intervertebral discs. Microscopic defects form in the spine due to malnutrition of the spinal discs. In these microscopic defects, areas of dead tissue are formed.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the spine
The main symptom of osteoarthritis is back pain, which can be continuous or periodic, painful or acute, often worse with sudden movement and physical activity.
Osteonecrosis is a common disease in athletes. It arises from the difference between physiological capacity and motor load, contributing to microtrauma and wear and tear of spinal tissue.
The localization of symptoms depends largely on the part of the spine where the pathological process occurs (cervical, thoracic, lumbar). If the pathological process is localized in several parts, this condition is called mixed osteoarthritis.
| Type of osteoarthritis | Cervical | Chest | lumbosacral | Mix |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical images |
|
|
|
the pain is stable or spreads to all parts of the spine. |
| symptoms |
|
|
compressive myelopathy (compression of the spinal cord by various tumors). |
All complications can occur with cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral osteoarthritis. |
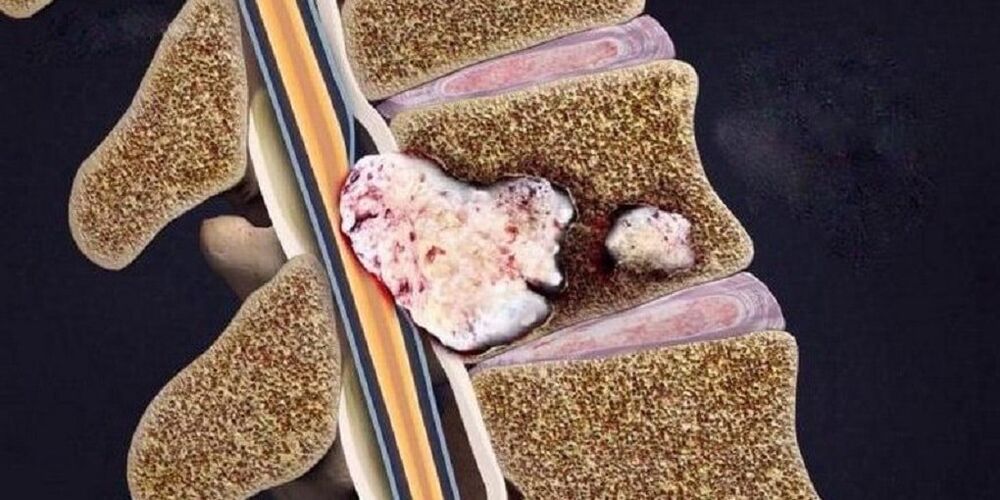
Stages of osteoarthritis
| Stage | Firstly | Monday | The third day | Wednesday |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changes in the spine |
|
|
Rupture and displacement of the spinal disc when other surrounding elements sink into its cavity, which causes the development of local inflammatory symptoms. | Destruction of other elements of the vertebral joints, pathological arrangement of joint surfaces, growth of marginal bones. |
| Patient complaints | There is no or signs of discomfort when staying in the same position for a long time. | Discomfort and pain with certain types of exercises. | Pain in the back, neck, lower back, sacrum or coccyx depending on location. | Constant pain throughout the spine. |
Differential diagnosis
- Acute myocardial infarction.The pain is concentrated in the heart area and only from there radiates (spreads) to the neck, lower jaw and arms. The disease begins for no reason or after physical activity with compression pain unrelated to movement in the spine. After half an hour, the pain reaches its maximum level, the patient has difficulty breathing and is afraid of death. Diagnosis is confirmed by electrocardiogram (ECG) and signs of myocardial necrosis.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage(hemorrhage between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater of the brain). In some cases, due to the toxic effect of blood spilling on the spinal roots, severe pain in the spine may occur. The main clinical sign is the presence of blood in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Spine abnormalities.Minimal examination: radiographs of the skull and cervical spine in anterior and lateral projections. The most common malformations of the spine are: fusion of the cervical vertebrae (first cervical vertebra) with the occipital bone, concavity of the edges of the occipital into the cranial cavity, fusion of the vertebrae, changes in shape. shape and size of vertebrae. vertebrae.
- Cervical lymphadenitismay also be accompanied by neck pain, sometimes aggravated by bending and turning. The diagnosis is not difficult: lymph nodes are enlarged, painful; a history of frequent sore throats.
- Multiple myeloma.Pain in the spine occurs gradually, against the background of progressive weight loss and periodic fever. The main test sign is protein in the urine.
- Tumor or metastasis in the spine.Evidence in favor of a malignant tumor is: gradually decreasing body weight, laboratory changes, as well as ultrasound of the sources of metastases - kidneys, lungs, stomach, thyroid, prostate.
- Rheumatoid polyarthritis and infectious-allergic arthritisDifferentiation is based on medical history, moderately increased body temperature and damage mainly to large joints.
- Depression wears a mask.Patients "impose" non-existent pathologies (in this context, symptoms of osteoarthritis), attempts to explain to them the essence of what is happening will encounter a wall of understandingwrong. Signs of hidden depression are: decreased mood, concentration and performance; sleep and appetite disorders; suicidal thoughts and actions.
- Gastric and duodenal ulcers, pancreatitis and cholecystitisdiagnosed by connecting pain with food intake, laboratory tests (FGDS, general blood tests, biochemical blood tests, activity of pancreatic enzymes, ultrasound examinationabdominal organs).
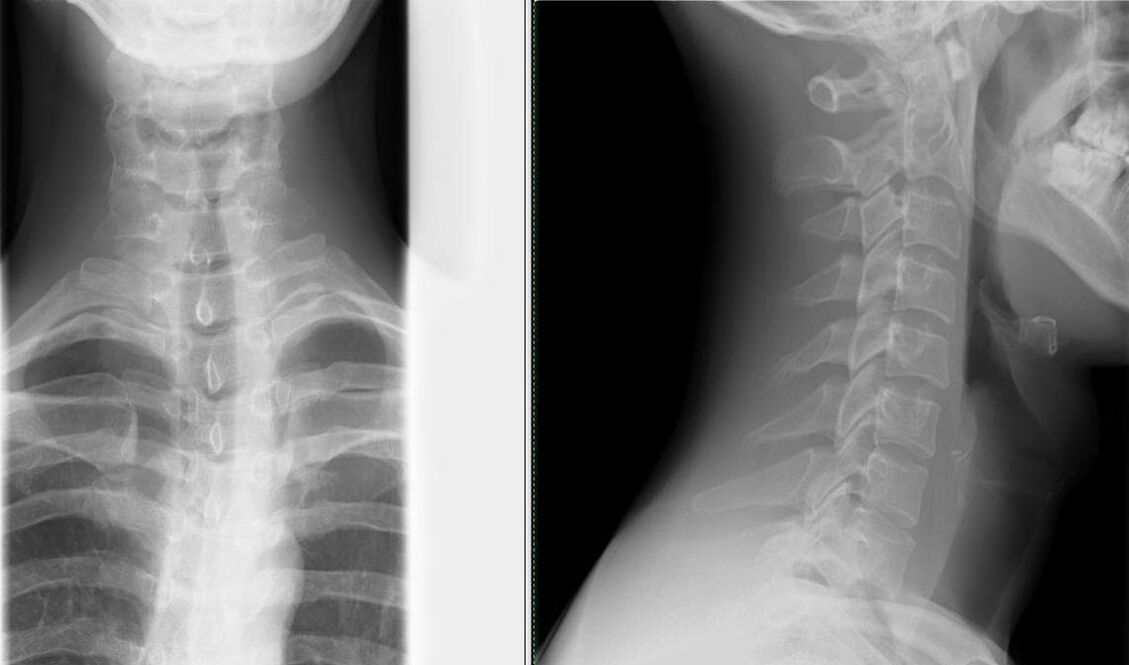
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
- Typically, the patient complains to a neurologist, who will collect a history of the patient's life and illness and conduct a neurological examination. A neurologist examines the spine in three options (standing, sitting, and lying down). When examining the back, pay special attention to posture, the lower angle of the shoulder blades, the iliac crest, the position of the shoulder girdle, and the expression of the back muscles. During palpation, deformation, pain and muscle tension are determined.
- When establishing the diagnosis of osteoarthritis, further consultation with specialists is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms (cardiologists, therapists, rheumatologists).
- Conduct mandatory laboratory tests (general blood tests, general urinalysis, biochemical blood tests).
- Studies confirm that the tool:
- X-ray of the spine in two views– the simplest method to determine changes in the spine (narrowing the distance between the vertebrae);
Depending on the extent, different changes are visible on X-ray:
Degree Firstly Monday The third day Wednesday X-ray signs There are no signs of radiation. Change the height of the disc. Protrusion (bulging into the spinal canal) of the intervertebral disc or even prolapse (loss). Formation of bone spurs (marginal bone growth) at the contact point of the vertebrae. - computed tomography (CT) and nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI)– is used not only to identify changes in the spine, but also to identify pathologies in other organs;
- USDG MAG (Ultrasound Dopplerography of the major arteries of the head)– ultrasound examination of the circulatory system in the head and neck, allowing you to diagnose the degree of vascular changes as early as possible.
- X-ray of the spine in two views– the simplest method to determine changes in the spine (narrowing the distance between the vertebrae);
What treatments are available for osteonecrosis?
Treatment with medicationshould be individualized and strictly differentiated, the prescription of medication is carried out by the doctor after diagnosis.
The main drugs used in the treatment of osteoarthritis:
- Pain relief is achieved with the help of analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Treatment with NSAIDs should be as short as possible, 5-7 days are enough to relieve pain. If your pain is poorly controlled and requires constant pain medication, you can take a selective COX-2 inhibitor.
- Antispasmodics relieve pain and reduce muscle spasms.
- Transdermal pain relief method: ointment, active ingredient is NSAID; anesthetic cream; application with anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs; Corticosteroids are added for greater effectiveness.
- Treatment aimed at regenerating inflamed or compressed nerves, as well as improving blood microcirculation: B vitamins, neuroprotectants, nicotinic acid.
- Oral cartilage protectants – glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate. They help prevent destructive changes in cartilage when used regularly. Chondroprotectors are incorporated into the cartilage tissue framework, thereby increasing bone matrix formation and reducing joint destruction. The most favorable composition: chondroitin sulfate + glucosamine sulfate + glucosamine hydrochloride + nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications are called combination chondroprotectors.
Non-drug treatments:
Neuro-orthopedic measures.An important point in the treatment of osteoarthritis is compliance with a reasonable physical activity regimen. Lying in bed for long periods of time with little physical activity is not only not beneficial for the spine, but also leads to a permanent symptom - back pain.
Exercise therapy (physical therapy)prescribed when the patient is in a stable state (especially during the period when the signs of the disease subside), the main goal is to strengthen the muscle corset.
To prevent falls, improve coordination of movements and functions of the vestibular apparatus (suitable for elderly patients), balance discs, platforms and paths are used in exercise therapy.
Manual therapywith severe pain in the neck. It is prescribed with particular vigilance and according to strict instructions. The main goal is to eliminate pathological mechanical changes in the musculoskeletal system. The main reason for prescribing manual therapy is pathological tension of the paraspinal muscles. Do not forget about some contraindications to this type of treatment, which are associated with osteochondrosis - large bone spurs (pathological growths on the surface of bone tissue), formed at the 4th stage of development of the bone. this pathology.
Physiotherapeutic procedures in the acute stage:
- supersonic;
- Phonetics;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- pulsed current;
- electrical nerve stimulation.
Physiotherapeutic procedures in the subacute phase:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic field therapy.
Massage.In all types, relaxing, superficial massage with rubbing elements is used. As soon as the pain symptoms are relieved with the help of massage, they will easily move on to stronger rubbing movements. When mastering the technique of acupressure massage (local), you should prioritize this type.
The issue of surgical intervention is decided strictly individually, depending on the indications and condition of the patient.

Preventive action

- Competent selection of furniture (especially in the workplace). The ergonomic chair has a flat and sturdy back. The bed includes a mattress of moderate hardness, pillows of moderate softness (if possible, mattress and orthopedic pillows).
- Adjust vision, posture, bite.
- Choose appropriate shoes (especially important for drivers). Maximum heel size is 5 cm.
- Wear a restraint belt, bandage, or corset while working.
- Adjust movements: avoid bending, turning, lifting weights with a straight back and legs bent at the knees.
- Change body position more often: do not stand or sit for long periods of time.
- Proper nutrition: limit eating sweet, salty, fatty, spicy foods. The most dangerous food for bones is white sugar because it removes calcium from bone tissue. The diet should include fruits, berries, vegetables, eggs, nuts, meat, kidneys, liver, fish, legumes and dairy products.
- Protect yourself from sudden temperature changes; hot water in bathtubs, saunas, swimming pools, etc. v. is especially dangerous because it relaxes the back muscles and not even a small injury is felt in this state, but leads to tragic consequences for the body. spine, and even more generally to the musculoskeletal system.
- Water procedures are not only a preventative measure but also a curative measure. Swimming combines stretching and muscle relaxation.
- Treatment of chronic diseases.
- Active and frequent vacations.
Examples of effective exercises to prevent cervical spondylosis, which can be done right at work:
- Sit in a chair, looking forward. The brush covers and supports the lower jaw. Press the head forward and down through resistance (tension phase); relax and stretch the neck muscles, slowly bringing the head back (relaxation phase);
- Sit in a chair, looking forward. Right palm placed on right cheek. Slowly tilt your head to the left, try to touch your left ear to your left shoulder and maintain this position for 3-5 seconds. Place the left palm on the left cheek and do the same with the right shoulder;
- Sit in a chair, looking forward. Hands placed on your knees. We tilt our head to the right, hold for 5-7 seconds and slowly return to the starting position. Then we tilt our head to the left and do the same.
Conclusion
The high frequency and social significance of osteoarthritis determine the scientific interest in this problem. This disease not only affects older people but is increasingly occurring in young people, attracting the attention of neurologists, neurosurgeons, orthopedic traumatologists and other specialists. another family. Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment of this pathology ensure social adaptation and quality of life in the future.